The
development life cycle represents the life of a system. These
systems will need to be:
•Designed
•Monitored
•Updated
•Replaced
all over a period of time.
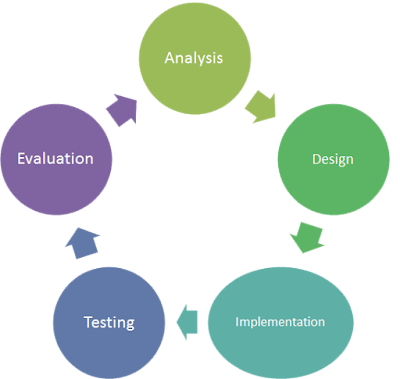
Stage 1: Analysis
Activities/processes
that are carried out in this stage are:
•Problem
statement - A report that highlights any potential issues
that could occur during the analysis and design of the systems.
•Interview
with the users - The
interviews are held with the users to determine whether they are willing to use
the systems, are they experienced enough or would they need training etc.
•Feasibility
study - The
people conducting the analysis look at the possibility of the project that they
are working on. For example, checking the resources that are available to them
(is the budget big enough?, do they have enough staff/time?)
Stage 2: Design
Activities/processes
that are carried out in this stage are:
•Process
description - Accurate and
detailed explanations of every process that is going to be occurring in the new
system. For example, database software that will be used for keeping records.
•Data
flow diagrams - These
provide a visual representation of the data flow travelling through a system.
This allows a user to get a much better understanding on the processes that
occur in a system.
•Data
dictionary - Is a
set of information that describes the content, functions and structure of a
system.
Stage 3: Implementation
Activities/processes
that are carried out in this stage are:
•Program
coding - In this stage, the actual installation of the system begins. The actual coding
of programs/applications will take place, using assets that have already been
produced (data dictionary, data flow diagrams etc.)
•Migration
of data - Means to transfer all the information from the original
system over to the one that is being put in place.
•Training
the users - Once this has all been done, the users would
need sufficient training in how to use these systems, based on the interviews
that were held earlier on the amount of time needed to train them may vary
depending on how inexperienced the users are with these systems.
Stage 4: Testing
Activities/processes
that are carried out in this stage are:
•Data
testing - Refers
to the testing of the information stored on the system (for example, programs
that have been installed onto the system, do they work? Is it suitable for the
user to use? Has all the data been transferred to the new system? Etc.)
•Compatibility
checks - Are
done to make sure that all the information/programs/applications that have been
installed onto the system can work properly on said system. As well as tests to
make sure that the user is able to work with the system (is it user friendly?
Are there any bugs in the system preventing them from being able to use it?
Etc.)
•Verification - The
system has to be verified that is 100% functional, is safe for users to begin
using, can support all the desired information etc.
Stage 5: Evaluation
Activities/processes
that are carried out in this stage are:
•Reviews - Once the system has been fully set up and declared available for use, a
review/reviews need to be conducted in order to reflect on how the design and
analysis of the system went. Was the budget big enough to support the project?
Were there enough resources? Did we meet all the goals for the project? How
closely were the steps of the development life cycle followed?
•Performance
monitoring - The
performance of the system will then be monitored for a period of time after the
user has began to work with it. This is to make sure that they have received
sufficient training in the use of the system, as well as to check if any
issues/errors crop up after the initial setup has taken place.
•Amendments - If
there are any problems detected in the performance monitoring, amendments will
need to be done in order to make sure that these issues are fixed and are
unlikely to occur again. Think of it as regular updates being applied to the
system.
Tools that can be used for Systems Analysis
A
data flow diagram is used as a representation of the data flow through a
system. These allow someone to see a process in the system from the viewpoint
of the data, as well as offering a visual representation of how a system
operates, what it accomplishes and how it will be implemented.
There
are 4 components in a DFD, these are represented by 4 symbols:
•External entities – The
source/destination of the data. Represented by squares.
•Processes – Such as
input/processing/output, these are represented by rectangles with rounded
corners.
•Data flow – Whether physical or
electronic data, this is represented by an arrow.
•Data stores – Physical/electronic
data stores are represented by open-ended rectangles.
CASE
(stands for Computer Aided Software Engineering) this is the use of computer
based design tools to help develop systems. By utilising these tools, analysts
are able to increase productivity and improve the quality of the pre-existing
systems as well as the new systems that are being designed.
SSADM
stands for Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method. This is an industry
standard that is developed for systems analysis in many government run
projects. SSADM combines both text and diagrams throughout the entire design
stage in the development life cycle, from the initial design idea of the system
to the systems’ physical design.
Many government run projects use SSADM
because they believe that, through the use of a professional, engineering tool,
they will be able to improve the overall quality of the systems that they are
designing.
There
are 7 steps to SSADM. These are as follows:
Feasibility
study – Is it possible to achieve what we want?
Investigation
of the current system – What needs to be improved in our design?
Business
systems operations – Does our organisation have the resources needed to support
this?
Requirements
specification – Do we have everything that we need to design these systems?
Technical
systems operations – Can we operate these systems?
Logical
design – Do we have a theoretical design that we want to use?
Physical
design – Does our physical design match the theoretical one and does it meet
our requirements?
Key Drivers
Key
drivers are reasons that can initiate the systems analysis and can eventually
lead to the design of new systems. These key drivers are:
Need
for growth - Expansion
of the business (for example, developing online sales, moving into a larger
work environment or expanding what the business does.)
Company
acquisition - Taking control of another business.
Increase
in productivity - Introducing
new ways of improving the efficiency of the business (for example, setting up
faster systems that require little human interaction to operate.)
Legal
requirements - Meaning
that, by law a new system would have to be implemented. For example, e-commerce
actions require an email as acknowledgement of an order.
Development Life Cycle Models
These
are models of systems analysis that closely follow the stages of the
development life cycle. They all vary in their approach to systems analysis,
and some are more appropriate in certain situations than others. We will be
covering three of the most widely used models.
Waterfall
Model – Used for projects that are short and easy, (the requirements are
understood by the user.) The
phases of this stage do not overlap (one must be completed before the next one
can begin.) After the end of each stage a review takes place to determine
whether or not the project is on the right track.
Rapid
Applications Development (RAD) – Used to quickly develop systems for low cost. In
this model every phase is developed in parallel with each other (as though they
were all smaller projects.) This reduces the development time as all the phases
are completed at the same time. Feedback from the users is encouraged.
Spiral
Model – Used for complex projects with a high risk and cost attached to them. While the risk of failure of the
project is high, a
large amount of risk analysis takes place in order to try and reduce that risk.
The software is developed very early on in the model, allowing for additional
functionality to be added later.
fakau
ReplyDeletemate same
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteGood articles, Have you heard of Mr Benjamin, Email: 247officedept@gmail.com --WhatsApp Contact:+1-9893943740-- who work with funding service they grant me loan of $95,000.00 to launch my business and I have been paying them annually for two years now and I still have 2 years left although I enjoy working with them because they are genuine Loan lender who can give you any kind of loan.
ReplyDeletehave you got assignment 2 for unit 11?
ReplyDeleteI am badr and i have aids
ReplyDeleteI dided form da aids
Delete